This is a short but hopefully complete walk through, which should help you getting started with coreboot(CB) and the IWILL DK8-HTX mainboard. It was written by Philipp Degler <pdegler {at} rumms.uni-mannheim.de> with the help of Mondrian Nuessle <mondrian {at} uni-mannheim.de>.
At the end of this tutorial you should be able to install coreboot on an IWILL DK8-HTX mainboard. You should also understand how to use different payloads.
Note: Another nice IWILL DK8-HTX tutorial has been written by Timo Schneider.
Requirements
You need the following software packages:
- coreboot v2 r2481 (You may also use newer versions. Anyway, this one is tested and working)
- A working development environment:
- make, gcc, etc. => gcc 3.3.x is known to work
- We used a SUSE Linux 9.1 with gcc 3.3.3
- Payloads:
- FILO 0.5 or greater (if using FILO)
- Etherboot 5.2.6
Hardware:
- Mainboard - IWILL DK8-HTX
- Debugging utility - RS232 DB-9 serial cross cable
- Flash utility - RD1 BIOS Savior (optional but could be helpful, especially in the case you do not want to take a risk!)
Important: You should build coreboot on a 32 bit platform!
Overview
OK, before we go into every detail you should get a rough overview of the "install" process. You don't need to go through the first 5 points if you have a working coreboot image. Unfortunately, the coreboot project is not distributing ready-made images (NOTE: This changed meanwhile. See [1]). There have already been discussions on the mailing list about that topic.
So, what will be your next steps?
- Get specific revision of coreboot
- Choose and build the payload
- Tweak coreboot config
- Build coreboot
- Check created ROM image
- Flash new BIOS - now it's getting dirty :)
- Verify your new BIOS
- Turn off your machine and start again
- After first boot, coreboot tables are in place and can be changed with the lxbios utility.
Getting coreboot source code
We recommend using coreboot SVN revision r2481.
$ svn co svn://coreboot.org/repos/trunk/coreboot-v2 -r 2481
Newer versions should also work fine.
$ svn co svn://coreboot.org/coreboot/trunk coreboot
will retrieve the newest revision.
Choosing a payload
coreboot alone is not able to boot your OS directly (bootstrap). Normally this is done by grub, lilo, ntloader or another bootloader. Unfortunately, coreboot is not providing a native 16 bit callback layer any more. As grub and others are depending on that layer you obviously can't use them together with coreboot. Therefore coreboot is offering an elf-loader that is able to load and start an elf executable. The elf image is put into the ROM together with the coreboot image. In context with coreboot this elf image is called payload. So finally the payload has the task to boot your OS. You can choose between a lot of different payloads. In this HOWTO we only mention FILO and Etherboot. These two will allow us to boot a Linux OS from local disk (IDE or SATA).
FILO (boot from IDE)
FILO sounds like lilo. In reality they have not so much in common. Both can boot an OS from IDE disk. As already mentioned earlier it is not possible to use lilo with coreboot directly. FILO is filling the gap. It is fully 32 bit and needs no BIOS callbacks like grub or lilo do. You should use FILO if you plan to boot from an IDE Disk or CDROM. Etherboot would also be able to boot from IDE but FILO standalone can read grub's menu.lst and generate a nice boot menu for you. Now please read the FILO article and build your elf image.
Maybe you will find our FILO config for DK8-HTX helpful:
# !!! NOTE !!! # Do NOT add spaces or comments at the end of option lines. # It confuses some versions of make.
# Use grub instead of autoboot? USE_GRUB = 1
# Grub menu.lst path MENULST_FILE = "hde2:/grub/menu.lst"
# time before default menu.lst is chosen. Set to 0 to ignore MENULST_TIMEOUT = 5
# Image filename for automatic boot and optional command line parameter #AUTOBOOT_FILE = "hda1:/boot/vmlinuz.suse initrd=/boot/initrd.suse pci=noacpi acpi=off root=/dev/hda2 console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 pci=lastbus=5" #AUTOBOOT_FILE = "mem@0xfff80000" #AUTOBOOT_FILE = "hde1@0" #AUTOBOOT_FILE = "uda1:/vmlinuz.elf"
# Time in second before booting AUTOBOOT_FILE AUTOBOOT_DELAY = 5
# Driver for hard disk, CompactFlash, and CD-ROM on IDE bus IDE_DISK = 1
# Add a short delay when polling status registers # (required on some broken SATA controllers) # NOTE: Slows down access significantly, so disable # whenever possible. #IDE_DISK_POLL_DELAY = 1
# Driver for USB Storage #USB_DISK = 1
# VGA text console VGA_CONSOLE = 1 PC_KEYBOARD = 1
# Serial console SERIAL_CONSOLE = 1 SERIAL_IOBASE = 0x3f8 # if SERIAL_SPEED is commented out, the speed will not be changed. SERIAL_SPEED = 115200
# Filesystems FSYS_EXT2FS = 1 #FSYS_FAT = 1 #FSYS_JFS = 1 #FSYS_MINIX = 1 #FSYS_REISERFS = 1 #FSYS_XFS = 1 #FSYS_ISO9660 = 1
# Support for boot disk image in bootable CD-ROM (El Torito) ELTORITO = 1
# PCI support #SUPPORT_PCI = 1
# Enable this to scan PCI busses above bus 0 # AMD64 based boards do need this. #PCI_BRUTE_SCAN = 1
# Sound support (needs SUPPORT_PCI) #SUPPORT_SOUND = 1
# Sound drivers #VIA_SOUND = 1
# Debugging #DEBUG_ALL = 1 #DEBUG_ELFBOOT = 1 #DEBUG_ELFNOTE = 1 #DEBUG_LINUXBIOS = 1 #DEBUG_MALLOC = 1 #DEBUG_MULTIBOOT = 1 #DEBUG_SEGMENT = 1 #DEBUG_SYS_INFO = 1 #DEBUG_TIMER = 1 #DEBUG_BLOCKDEV = 1 #DEBUG_PCI = 1 #DEBUG_VIA_SOUND = 1 #DEBUG_LINUXLOAD = 1 #DEBUG_IDE = 1 #DEBUG_USB = 1 #DEBUG_ELTORITO = 1
# i386 options
# Loader for standard Linux kernel image, a.k.a. /vmlinuz LINUX_LOADER = 1
# Boot FILO from Multiboot loader (eg. GRUB) #MULTIBOOT_IMAGE = 1
Etherboot (boot from SATA)
Etherboot is an independent open source project. It allows one to boot an OS from various media:
- floppy
- CDROM
- HDD
- USB
- most network interfaces (of course).
Etherboot also supports PXE (Preboot Execution Environment). Why is etherboot interesting in this HOWTO? Well, etherboot also supports SATA. This is because an earlier modified FILO version was integrated into etherboot. More details on building an etherboot for coreboot are available.
Hints
How can I choose the driver for my network interface (if)?
If you want to add support for more than one if-driver use '--' to separate the options from each other. In the example underneath we are compiling etherboot with Intel® 82541PI and FILO support. "*.zelf" states that we want to build a compressed image which is normally a good idea.
$ make bin/e1000--filo.zelf
But how do I know the name of the driver for my network if?
In etherboot most drivers cover a whole family of cards. This means you have to find out which driver family is supporting your specific device. So here is what you do:
- Change to the "src" directory of etherboot and run "make" without any arguments. This will generate a NIC file in the "bin" dir.
- Change to the "bin" dir and open the NIC file with your favorite editor. You should find the matching family name to your device.
Configuring coreboot
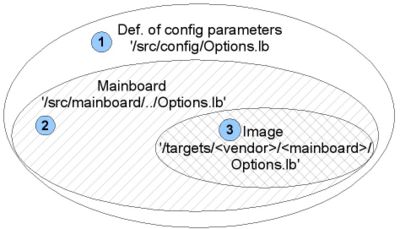
As you can see in the graphic the config space of coreboot can be divided in 3 sets. Each set comprises a number of configuration options.
- Set of all Config options (1)
- Typically a coreboot developer adds or changes config options during the process of development. The support of new chips and functions often leads to new config options.
- Set of Mainboard options (2)
- This is a subset of all existing Options. If one ports a mainboard for LB one has to decide which config options are needed in order to model the architecture of the mainboard. The maintainer sets default values that should ensure a working version for the respective mainboard.
- Set of Image options (3)
- Finally the image specific options are a subset of the mainboard specific options. They allow endusers to override default values. Although one can override any option the mainboard maintainer has defined it is not a good idea to do so. One should only override options that regard image settings. For example which payload to use.
In this HOWTO we want to concentrate on the image config. Normally you would only need one image to boot your PC, but changing configuration may lead to a broken BIOS. For this reason coreboot offers a fallback mechanism, that jumps into place if your normal coreboot image would not boot. We will see later how you can boot with a specific image (normal or fallback).
Specify Log-Level
Normally LB can boot really fast — a lot of log messages may really slow it down. You can choose between 9 different loglevels:
- EMERG — system is unusable
- ALERT — action must be taken immediately
- CRIT — critical conditions
- ERR — error conditions
- WARNING — warning conditions
- NOTICE — normal but significant condition
- INFO — informational
- DEBUG — debug-level messages
- SPEW — way too many details
You may change the default loglevel (8) by adding the following two lines to your "targets/iwill/dk8_htx/Config.lb"
## Request this level of debugging output default DEFAULT_CONSOLE_LOGLEVEL=5 ## At a maximum only compile in this level of debugging default MAXIMUM_CONSOLE_LOGLEVEL=5
VGA Support
Before one can access the VGA device it has to be initialized. In LB you can choose between two options:
- Use the original proprietary ATI BIOS.
- or use a LB open source driver if there is one. Otherwise you have to implement your own driver.
In this HOWTO we will concentrate on the first option, because this will add full support for the VGA onboard device.
Image Config (targets/iwill/dk8_htx/Config.lb)
The original ATI BIOS has to be prepended to the coreboot.rom. Therefore you have to change the size of the coreboot.rom. Add the following lines to your Config.lb:
- reserve 36k for VGA extension ROM
option ROM_SIZE = (512*1024)-(36*1024)
As you can see we are reserving 36KB for the VGA BIOS.
Mainboard Config (src/mainboards/iwill/dk8_htx/Config.lb)
Normally you should not change the mainboard config because mainboards do not change that often. In case of VGA support we need to make some modifications so that coreboot will know where to load the VGA BIOS from. So please add the following node (the italic lines) to the "device tree" of the mainboard's Config.lb.
...
- PCI bridge
device pci 0.0 on
device pci 0.0 on end
device pci 0.1 on end
device pci 0.2 off end
device pci 1.0 off end
chip drivers/pci/onboard
device pci 6.0 on end
register "rom_address" = "0xfff80000"
end
end
...
Hints
- How would I know the size of my VGA BIOS and how do I get it?
- => The VGA support HOWTO will answer this question.
- The VGA BIOS image that I extracted with "dd" is not working. What else can I do?
- => Sometimes not the complete VGA BIOS image is available via /dev/mem. In this case you better use AmiDeco tool of Anton Borisov. Read the VGA section of the Tyan S2882 Build Tutorial on how to use it.
Building coreboot
You have compiled your payload and changed Config.lb of your target mainboard accordingly. So you are now ready to make the next step.
Start the build process
- cd to "targets" dir
- run "./buildtarget producer/mainboard_model"
- The result should be a build directory. In this case a new dir called "dk8_htx".
$ ./buildtarget iwill/dk8_htx
- cd to new dir "iwill/dk8_htx/dk8_htx"
- run "make"
- Depending on your image config (Config.lb) a normal-, a fallback- and maybe a failure-image will be compiled. Finally these separate images will be concatenated to a final coreboot.rom".
Append VGA BIOS
If you are not planing to use VGA you can leave out this part of the HOWTO.
Do you remember the configuration chapter where we reduced the size of the coreboot.rom image about 36KB. Now we have to concatenate VGA BIOS image and coreboot image. We assume the name of your VGA BIOS image is "ati_bios.rom".
- copy ati_bios.rom into the build directory
- cd to build directory "targets/iwill/dk8_htx/dk8_htx"
- use "cat" to concat the two images
$ cat ati_bios.rom coreboot.rom > final.rom
Check the image file
Before burning the final image it is always a good idea to check the image size. DK8-HTX has a 512KB ROM. So the "coreboot.rom" ("final.rom" respectively) should also have 512KB.
Hints
coreboot is not compiling?
Sometimes scripts use standard output of a command to decide for example if a library has the right version. Actually this is not good style and you should post such issues if you find some. But one could solve such problems by changing console language to English. This can be done for example in your local .bashrc:
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells. ... LANGUAGE=en_EN.utf8 ....
Installing coreboot
Up till now we only looked at the software part of this HOWTO. The next steps may involve a little bit of hardware. We used a BIOS Savior in order to safely install and develop coreboot. Other options include FLASH/ROM emulators and external FLASH/EPROM programmers. If you simply want to use coreboot as "normal" BIOS replacement you could skip the next paragraph and continue with compiling the flashrom utility.
The BIOS Savior

We used a BIOS Savior for development purposes. Unfortunately it is hard to get the right model in Europe. So we got ourselves a similar model and modified it a "little". Actually this was quite a hack and should not be repeated. Try to get the right one for a PLCC32 socket. The ROM chip is produced by SST and its name is "49LF004B". The BIOS Savior is produced by IOSS they provide a list to find the right RD1 Savior. As you can see on the picture on the right hand side the RD1 is a sandwich consisting of two chips. One is your original chip and one is an internal chip that comes together with the savior. Once your System is up and running you can choose between one or the other by using a dip switch. Some people on the mailing list reported problems with the quality of the internal flash part. Therefore, one would copy the original BIOS image to the internal flash part and then always (re)flash the original mainboard ROM chip. Of course you should have tested both options with the original BIOS before you really start your development. Please also read the FAQ regarding this topic.
There are also a lot of other tools that could be helpful, especially if you plan to join LB development. See here for more info.
Compiling the flashrom utility
Make sure the packages pciutils and pciutils-devel are installed on your machine.
- cd to "util/flashrom"
- type "make"
- the result should be a "flashrom" executable
- you can test the flashrom with your ROM chip
$ ./flashrom -V Calibrating delay loop... Setting up microsecond timing loop 614M loops per second ok ... ... Trying SST49LF004A/B, 512 KB probe_jedec: id1 0xbf, id2 0x60 SST49LF004A/B found at physical address: 0xfff80000 Flash part is SST49LF004A/B OK, only ENABLING flash write, but NOT FLASHING.
- Make sure your ROM chip is detected (supported).
Flashing the new image
- Before you start flashing, you should use flashrom to save the original BIOS image.
$ ./flashrom -r orig.rom
- Now switch your BIOS Savior to "RD1". If you don't have a BIOS Savior you can also use another ROM chip and replace the original one while the system is up and running (hot-swapping). ATTENTION: Changing hardware while system power is on often bares the risk of damaging something. We warned you! It is your risk!
- Time to flash the new image
$ ./flashrom -c SST49LF004A/B -V -w ../../targets/Iwill/dk8htx/dk8htx/coreboot.rom
- Just to make sure, verify your ROM image
$ ./flashrom -c SST49LF004A/B --force -v ../../targets/Iwill/dk8htx/dk8htx/coreboot.rom
- You did it :) Now power off your machine and restart it.
- LB should come up and load your payload.
Modifying LB tables with lxbios
After the first boot with coreboot, it is saving information and configuration data. This data can be viewed and tweaked with a utility called lxbios. Show all available parameters/data:
$ lxbios -a
Set a parameter to specific value. In this example set default boot to "normal" image.
$ lxbios -w boot_option=Normal
Hints
- Where can I download lxbios?
- => have look at sourceforge.net.
- I switched to "Normal" image with lxbios but it is not booting correctly.
- => after three successless boots the fallback mechanism sets in and tries to boot the fallback image.
Contributed by Philipp Degler <pdegler (at) rumms (dot) uni-mannheim (dot) de>

|
This work is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, version 2. This work is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. |